

In the United States, the hydrocarbon dew point of processed, pipelined natural gas is related to and characterized by the term GPM which is the gallons of liquefiable hydrocarbons contained in 1,000 cubic feet (28 m 3) of natural gas at a stated temperature and pressure.

The hydrocarbon dew point of a gas is a different concept from the water dew point, the latter being the temperature (at a given pressure) at which water vapor present in a gas mixture will condense out of the gas. The hydrocarbon dew point is universally used in the natural gas industry as an important quality parameter, stipulated in contractual specifications and enforced throughout the natural gas supply chain, from producers through processing, transmission and distribution companies to final end users.
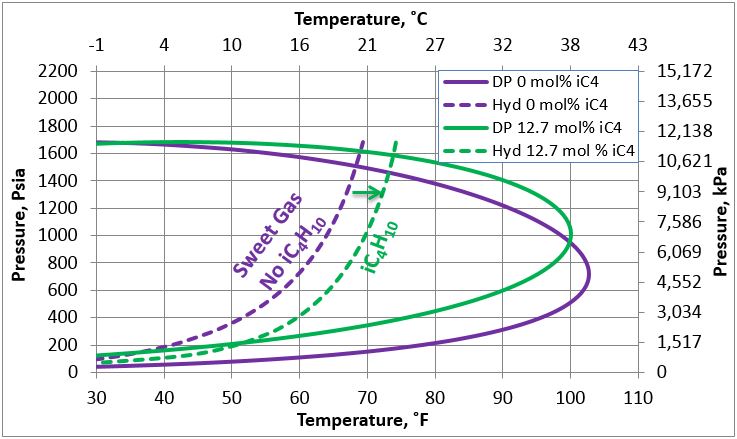
The hydrocarbon dew point is a function of the gas composition as well as the pressure. The maximum temperature at which such condensation takes place is called the cricondentherm. It is often also referred to as the HDP or the HCDP. The hydrocarbon dew point is the temperature (at a given pressure) at which the hydrocarbon components of any hydrocarbon-rich gas mixture, such as natural gas, will start to condense out of the gaseous phase.
#HYDROCARBON DEW POINT CALCULATOR EXCEL FULL#
This finally demonstrate the full image of the petroleum refinery processes importance to the local and international world of petroleum and petrochemical industries and human’s life.For the meteorological dew point, see Dew point. It covers refinery classification, crude oil structure and economics, in addition to the refinery processing line from the beginning of the handling of the feed introduced to plant units passing through the desalting, preheating, flashing units till reaching the separation processes in distillation towers producing the refinery products, vacuum tower distillation and the naphtha processing using the modern technique Methaforming that are all discussed theoretically and simulated for a real-life Petroleum Plant Production Units using the industrial simulating programs. This book discusses the full aspects concerning the Petroleum Refinery starting from its history reaching a plant design for the products refinery processes and naphtha processing with the help of an industrial simulation programs such as Aspen HYSYS. These decisions have to take into account uncertainties and constraints in factors such as the source and availability of raw material, production and distribution costs and expected market demand. These factors and others forced petroleum companies for a greater need in the strategic planning optimization and sensitivity analysis in order to make decisions that satisfy conflicting multiobjective goals of maximizing expected profit while simultaneously minimizing risk.

It is facing a challenging task to remain competitive in a globalized market, the fluctuating demand for petroleum products and the current situation of fluctuating high petroleum crude oil prices is a demonstration that markets and industries throughout the world are impacted by the uncertainty and volatility of the petroleum industry. In the recent years, petroleum industry has grown increasingly complex as a result of tighter competition, stricter environmental regulations and lower-margin profits. Petroleum industry has a major share in the world energy and industrial markets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
